Testosterone levels drop at a rate of 2% per year after 30 years of age, but most men are not aware of this fact. It is produced primarily in the testes and is responsible for development and function of various organ systems early in life, especially during puberty; although the impact and effects are not confined just to the teenage years-it determines your daily functional capacity.
Testosterone is essential in all stages of adulthood. Most notably, it is the key determining factor in maintaining muscle and bone strength, red blood cell production, sex drive (libido), and sperm count refresh. If you have been feeling tired throughout the day, have been feeling more fatigued despite no significant changes in your daily routine, or struggling with motivation of personal goals of professional ambitions, low testosterone (Low T) could be the silent contributing factor.
There has been an almost epidemic level of testosterone deficiency in the US with a growing prevalence within the past decade due to various environmental factors of progresive industrialization (victims of our own success),Testosterone replacement therapy has become the solution available for men to regain their health and fight back. The marquee medication has been testosterone cypionate due to the reliability and it being one of the longest studied therapies in athletes. TRT treatment online is generally safe under supervision, but it is not risk-free.
Before we discuss how to boost T levels, it is worth looking at how testosterone levels change with age and generally after 40 and when there is a point to intervene.
Testosterone Levels by Age in Men
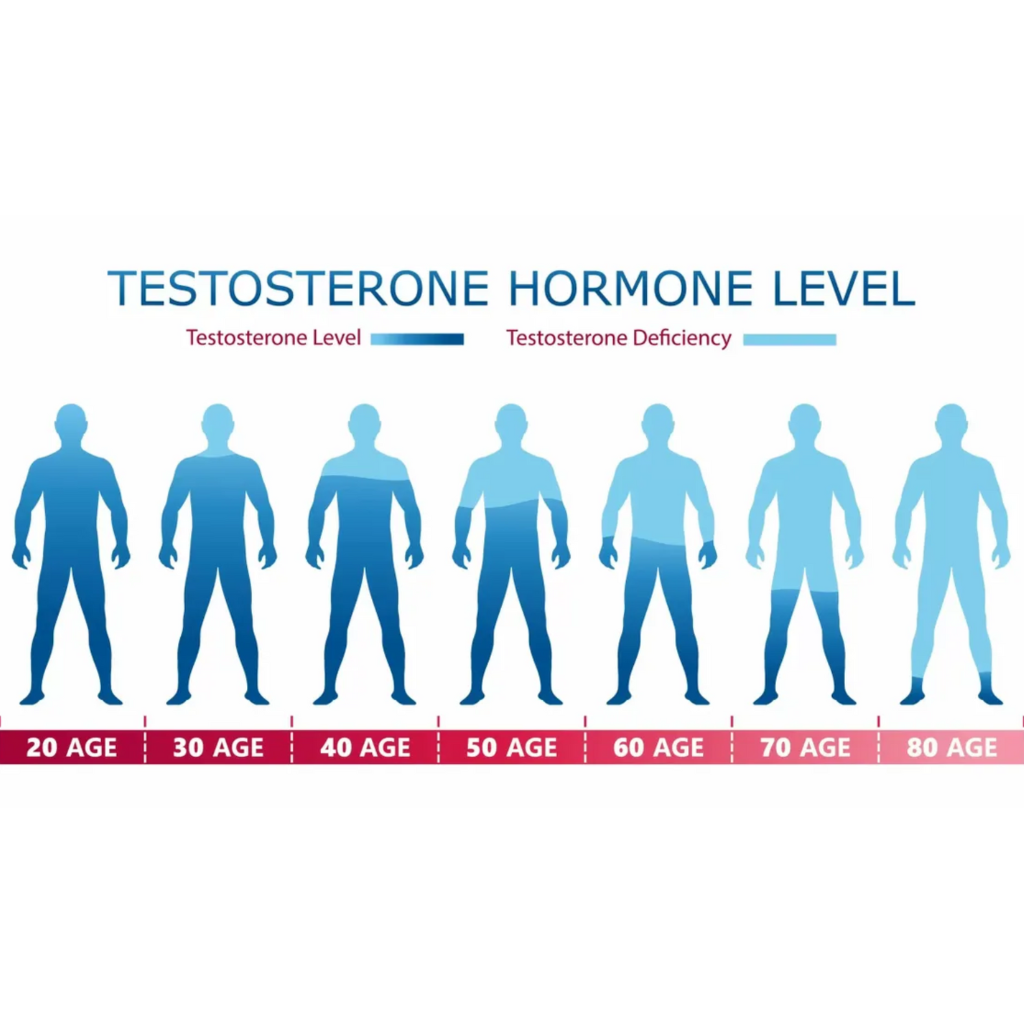
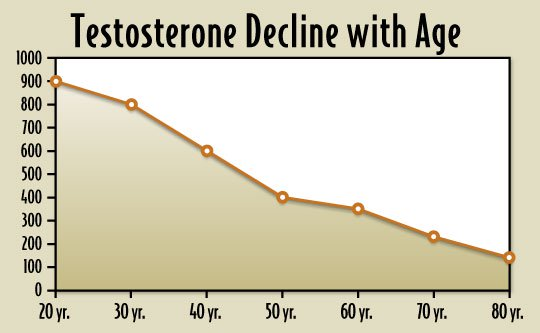
There is a normal cyclical lifecycle of testosterone production within the body. Specifically, T levels spike during puberty with a flood of hormone release through the HPG axis. The peak is usually reached in the late teens to mid twenties. After the peak, testosterone levels slowly start declining in mid thirties, with the decline continuing at a steady rate through end of life.
According to epidemiological studies reported on Healthline, by the age of 70, the typical male's testosterone production will be 30% less than it was at its peak.
Here are the approximate ranges for average total testosterone by age (ng/dL):
|
Age Range |
Average Total Testosterone |
|
Teens (14–19) |
300–1,200 ng/dL |
|
20–29 |
300–1,000 ng/dL |
|
30–39 |
300–950 ng/dL |
|
40–49 |
250–900 ng/dL |
|
50–59 |
215–850 ng/dL |
|
60+ |
200–700 ng/dL |
According to a study, the normal range for total testosterone in healthy adult males between the ages of 40 and 70 is generally between 196 and 916 ng/dL. These levels fluctuate slightly depending on the lab and method of measurement. However, the critical point to note is this: although there is a range, clinical symptoms are more important than the number alone:
-
There is also the matter of differentiating free testosterone from total testosterone.
-
Total testosterone refers to the amount of testosterone present in the blood. This is regardless of whether it is bound or free.
- Free testosterone is the amount available for immediate use by the body.
Some men can have "normal" total testosterone but low free testosterone, and still experience the symptoms. That's why lab results + symptom monitoring is a better indication than numbers alone.

Signs of Low Testosterone Levels
Low testosterone doesn't necessarily come on like a sledgehammer. For most men, it sneaks up on them. You may begin to notice persistent fatigue and a lowered interest in activities. Workouts don't quite feel the same. Not quite what it used to be.
It could be aging, workplace stress, or poor sleep. But if symptoms persist, it could be low testosterone (Low T). Some common symptoms of Low T:
- Persistent fatigue, even after rest
- Lower libido or performance dysfunction
- Difficulty with erections or softer erections
- Loss of muscle or delayed strength
- Excess body fat is typically visible in the midsection.
- Mood swings, irritability, or a slight depression.
- Loss of concentration or clear thinking (brain fog).
- Lack of motivation or confidence.
- Poor-quality sleep on occasion.
- Hair thinning on the body or face.
These issues can significantly impact personal relationships, as you will notice a difference in your work life and self-esteem.
Suppose you said "yes" to several of these, your next step would be to have your T levels measured and checked. Knowing your T levels is important and usually needs to be done my men by themselves as many primary care physicians will not order the test due to insurance denials. The insurance companies are notorious for making extremely long paperwork and challenges for physicians to order any tests that might be more expensive; you will want to be sure to get a testosterone level test. An at-home simple blood test can confirm the actual presence of this condition (medically called hypogonadism). Knowing your T levels is the first step to determine the best next course of action, don’t ignore these signs of low TRT.
What Makes Testosterone Levels Drop Faster by Age
Although testosterone levels decline with age, some factors can cause this drop to be more precipitous than it should, often by a SIGNIFICANT amount. Some 21st century lifestyle habits that have been known to be especially detrimental to hormonal wellness include:
- Insufficient sleep and sleep apnea
- Higher levels of stress (which increase the levels of cortisol)
- Physical inactivity or too much sitting (desk jobs)
- Overweight, obesity and high BMI
- Higher sugar and refined food diet (processed foods)
- Heavy use of alcohol
- Illicit drug use, tobacco, and vaping
- Certain medications (e.g., antidepressants or opioids)
Most often, it is not a single big problem, but a lot of small habits that have formed over the years. The good news is that most of them can be fixed. Sleeping better, losing weight, and exercising can naturally increase testosterone levels. But for others, even with the life adjustments, levels stay low, and that is when TRT might come into the picture.
Natural Ways to Support Healthy Testosterone Levels in Adulting Men
Before we cover medications, it's helpful to go through what you can do naturally without a prescription medication to improve hypogonadism. Minor everyday habits changes in daily routines may sometimes amount to a big change, particularly if your levels are borderline low.
The following are some good ways to augment your body's testosterone production:
Lift heavy weights
Strength training, particularly compound exercises such as squats, deadlifts, and presses. It naturally causes your body to increase testosterone levels.
Prioritize sleep
Most of the testosterone is secreted during deep sleep. Target 7–8 hours each night. Poor sleep ultimately leads to lower testosterone levels.
Consume more healthy fats
Testosterone is synthesized from cholesterol. Set your menu with items like whole eggs, avocado, olive oil, nuts, and oily fish.
Reduce excess fat
Especially around your belly. Adipose tissue converts testosterone into estrogen, resulting in a hormonal imbalance.
Get sunlight
Vitamin D controls testosterone levels. In case you can't go outdoors enough, a supplement may be supportive.
Reduce stress
Cortisol rises in response to stress and directly lowers testosterone levels. Go for a walk every day. Breathe deeply. Step away from your computer screen.
Avoid plastics and chemicals
Avoiding BPA (Bisphenol-A) will be helpful (contained in plastic water bottles and all kinds of food containers). The changes alone may not completely restore testosterone levels, but they can certainly help with significant weight loss, thereby promoting overall health.
Regardless of the method you choose, make sure that you follow up properly. Frequent blood tests maintain hormone levels in an optimal range. This ensures that the body will respond well to treatment.
For some men, these lifestyle changes will be enough to start recovering. For others, especially those with extremely low levels or very severe symptoms, TRT may still play an important role.
You may also read: 6 Foods to Increase Your Testosterone
Best TRT Treatment Options for Men
Testosterone replacement therapy is far from being a cookie-cutter solution for all men. The first branch point to consider is that there are various methods of delivery. The choice depends on your lifestyle, comfort, and the physician's recommendations.

1. Testosterone Cypionate
This is one of the most reliable and most commonly used methods. Administering 200 mg of testosterone cypionate via injection on a weekly basis is the most frequent dosing to treat hypogonadism. You can go into a local clinic to have this done weekly, or more commonly self-inject via sterile technique taught to you by a healthcare provider into your muscle, usually into the thigh or the glute.
2. Gels & Creams
Used each day on the skin. Simple to use, but can be passed to others through skin contact (not recommended in the presence of children or partners). Also, there is variation in absorption.
3. Patches
Applied on the skin, typically to the back, thigh, or arm, and used each day. It can irritate the skin in some individuals.
4. Pellets
Small pellets are implanted beneath the skin (usually in the hip region). Release testosterone for 3–6 months. It is considered a bedside surgical procedure and almost never used in the US due to the side effects and complications profile.
5. Oral Tablets or Buccal Tablets
Oral trt is also available to improve the TRT levels. Previously, this was not used commonly as the oral testosterone formulations were known to be hepatotoxic, although now are becoming more popular as the newest FDA approved oral testosterone medications no longer have that side effect.
Regardless of the method you choose, make sure that you follow up appropriately. Frequent blood tests and having a doctor review your clinical journey will help to maintain hormone levels in an optimal range; ensuring that the body will respond well to treatment.
Also Read: Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) vs. Natural Methods for Boosting Testosterone
TRT Levels Boost Timeline
Don't anticipate instant, magical results. Some men notice changes in the first two week, starting with mental health benefits. Listed below is an average generalized timeline, although it is important to note that individual results may vary:
1–2 weeks:
Improved mood, energy, and sleep. Men start feeling more motivated, energized, and focused.
3–6 weeks:
Improved sexual drive/libido, and better erectile quality. You may start to even have more frequent morning erections.
6–12 weeks:
Improved body composition with higher muscle tone, and lower fat percentage. Although testosterone is not a weight-loss medication, men will start seeing a lower body fat percentage as more of their food will be used for muscle production rather than adipose tissue building.
3–6 months:
Ongoing improvement in strength, endurance, and mood stability.
6–12 months:
Longer term benefits include improved bone density and potentially better recovery of joints with consistent optimized testosterone levels leading to a boost in confidence.
Keep in mind that everything is individual for every man based on age, starting T levels, lifestyle, and condition. Regular blood testing keeps you at the right level without going over.
TRT is not just about body changes; it also works to sharpen the brain and improve overall health. Greater emotional equilibrium. That's the true victory.
Do Any Risks or Side Effects exist with TRT?
Just like any form of medical treatment, testosterone replacement therapy has its own risks (otherwise it would be an over-the-counter medication!); especially when T levels are not well monitored through your journey. However, if you are under good medical care, you can reassess how your body is responding and adapt treatment easily.
Potential side effects are:
- Acne or oily complexion
- Too high red blood cell count (can increase risk of blood clots if not controlled)
- Worsening of sleep apnea (if present)
- Testicular atrophy
- Suppression of natural testosterone production
- Decreased sperm count (significant if you are planning to have children in the next 12 months)
- Swelling or water retention
- Mood changes (if your dosing is not perfected)
Monitoring regularly, particularly in the initial 3–6 months, is essential. The majority of physicians will conduct tests to monitor your:
- Total testosterone and free testosterone
- Estrogen levels (men need balance here as well)
- Blood pressure
- Hematocrit (red blood cells)
- PSA (prostate health)
People afflicted with some medical issues, such as prostate cancer, untreated sleep apnea, or severe heart problems, should never be given TRT. Hence, for its safety, the necessity of a legitimate doctor, whether virtual or not, is never to be compromised.
Side effects must be monitored, even if most are manageable. In almost every case, they can be dealt with via dosage alteration, working on lifestyle adjustments, or balancing hormones through medications such as aromatase inhibitors.
The risk does exist when it comes to TRT, but it can be mitigated when the treatment is done correctly and monitored by sound medical practice. It usually poses less risk than living with the long-term effects of low testosterone.
Last Thoughts
If you're in your 30s, 40s, or older and starting to feel "off", tired, less motivated, experiencing problems with motivation or sexual health, it may be time to get your testosterone checked.
Low T is more prevalent than most men realize. And although aging is unavoidable, being weak, moody, and uninterested in life isn't something you must live with. At Forty Health, we do not advertise miracles for sale. We provide real solutions with a solid evidence-based medical foundation.
Are you thinking of testosterone cypionate 250 mg or simply aiming to understand your hormonal health better? Then rest assured that our experts and board-certified clinical team will be by your side the whole way. Start with a simple blood test. See your numbers. Talk to our specialists. Feel like yourself again.